ADB Support for Regional Public Goods
Rapid economic growth and regional integration has led to increasing cross-border challenges for developing countries—such as controlling communicable diseases, facilitating trans-border infrastructure, mitigating financial contagion, and addressing environmental concerns—which require regional responses. The role of regional development banks (RDBs) in supporting regional public goods (RPGs) is significant. RDBs have scaled up assistance and partnered with developing member countries (DMCs) in promoting regional cooperation and integration (RCI) that promote RPGs.
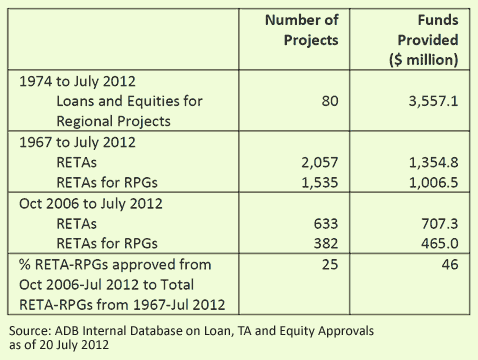 ADB’s support for RPGs was integrated in its RCI Strategy (adopted in 2006) which identified RPG as one of four interrelated pillars. RPGs are defined as a benefit shared by two or more countries in the region, focusing on four key areas: (i) the environment, communicable diseases, natural disasters, clean energy and energy efficiency, governance, and human and drug trafficking; (ii) research; (iii) capacity building and institutional strengthening; and (iv) regional partnership. While lending for RPGs is limited, the majority of ADB’s RPG projects fall under regional technical assistance (RETA) and grants (or grant-financed projects), covering subregions such as ASEAN (ASEAN+3), CAREC, GMS, and SASEC. ADB’s support for RPGs has increased significantly since 2006, with nearly half of funds allocated to RPGs from 2006 to July 2012 implementing the RCI Strategy. The establishment of the PRC Poverty Reduction and Regional Cooperation Fund (2005), the Regional Cooperation and Integration Fund (2007), and the Investment Climate Facilitation Fund (2008) have significantly increased support for RPGs.
ADB’s support for RPGs was integrated in its RCI Strategy (adopted in 2006) which identified RPG as one of four interrelated pillars. RPGs are defined as a benefit shared by two or more countries in the region, focusing on four key areas: (i) the environment, communicable diseases, natural disasters, clean energy and energy efficiency, governance, and human and drug trafficking; (ii) research; (iii) capacity building and institutional strengthening; and (iv) regional partnership. While lending for RPGs is limited, the majority of ADB’s RPG projects fall under regional technical assistance (RETA) and grants (or grant-financed projects), covering subregions such as ASEAN (ASEAN+3), CAREC, GMS, and SASEC. ADB’s support for RPGs has increased significantly since 2006, with nearly half of funds allocated to RPGs from 2006 to July 2012 implementing the RCI Strategy. The establishment of the PRC Poverty Reduction and Regional Cooperation Fund (2005), the Regional Cooperation and Integration Fund (2007), and the Investment Climate Facilitation Fund (2008) have significantly increased support for RPGs.
Increased globalization and regionalism have important implications for Asia and the Pacific, notably in responding to natural disasters, environmental concerns, and demands for knowledge dissemination. In more effectively meeting these challenges, ADB has a increasing role to play in providing RPGs through raising lending for regional projects and advancing knowledge dissemination on RCI. ADB intends to boost work in addressing regional food security and labor migration.




