Trade Indicators
- Export growth
- Export intensity index
- Export share
- Import growth
- Import share
- Intra-regional trade intensity index
- Intra-regional trade share
- Total trade
- Trade growth
- Trade intensity index
- Trade share
- Trade openness
Foreign Direct Investment Indicators
- Inward FDI flows (BOP) in million US$
- Inward FDI flows (BOP) in % to total
- Inward Direct Investment Positions, in million US$
Money and Finance Indicators
- Bond Market Rates
- Lending Market Rates
- Money Market Rates
- Stock Market Returns
- Coefficient of Variation
- Coefficient of variation of bond market rates
- Coefficient of variation of lending market rates
- Coefficient of variation of money market rates
- Portfolio Investment Assets
- International Debt Securities
Movement of People Indicators
Trade Indicators
Note: Total trade data are sourced from the International Monetary Fund Direction of Trade Statistics (DOTS), except data for Taipei,China which are sourced from the CEIC Data. Total trade data are available for ADB regional member economies except Bhutan, Cook Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Nauru, Palau, Timor-Leste, and Tuvalu. The commodity trade data are from the United Nations Commodity Trade Statistics (UN Comtrade) Online Database. They are based on the Harmonized System (HS) 1996 classification. Data availability varies across economies. Download data availability matrix.
-
Export growth is the percentage change in the value of exports relative to the previous year.
Export intensity indexis the ratio of a trading partner’s share to a country/region’s total exports and the share of world exports going to the sametrading partner. It is calculated as:
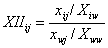
where xij is the dollar value of exports of country/region i to country/region j, Xiw is the dollar value of the exports of country/region i to the world, xwj is the dollar value of world exports to country/region j, and Xww is the dollar value of world exports. An index of more than one indicates that trade flow between countries/regions is larger than expected given their importance in world trade.
Export share is the percentage of exports going to a partner to total exports of a country/region. It is computed as the dollar value of exports of country/region i to country/region j expressed as a percentage share of the dollar value of exports of country/region i to the world. A higher share indicates a higher degree of integration between partner countries/regions.
Import growth is the percentage change in the value of imports relative to the previous year.
Import share is the percentage of imports from a partner to total imports of a country/region. It is computed as dollar value of imports of country/region i from country/region j expressed as a percentage share of the dollar value of imports of country/region i from the world. A higher share indicates a higher degree of integration between partner countries/regions.
Intra-regional trade intensity index is the ratio of intra-regional trade share to the share of world trade with the region, calculated using trade data. It is computed as:
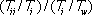
where Tii is exports of region i to region i plus imports of region i from region i; Ti is total exports of region i to the world plus total imports of region i from the world; and Tw is total world exports plus imports. It determines whether trade within the region is greater or smaller than should be expected on the basis of the region's importance in world trade. An index of more than one indicates that trade flow within the region is larger than expected given the importance of the region in world trade.
( Last update : 31 Oct 2013 )Intra-regional trade share is the percentage of intra-regional trade to total trade of the region, calculated using trade data. It is calculated as:
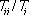
where Tii is exports of region i to region i plus imports of region i from region i and Ti is total exports of region i to the world plus total imports of region i from the world. A higher share indicates a higher degree of dependency on regional trade. ( Last update : 31 Oct 2013 )
Total trade is the sum of the value of exports and imports.
Trade growth is the percentage change in the value of total trade relative to the previous year.
Trade intensity index is the ratio of a trading partner’s share to a country/region’s total trade and the share of world trade with the same trading partner. It is calculated as:
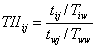
where tij is the dollar value of total trade of country/region i with country/region j, Tiw is the dollar value of the total trade of country/region i with the world, twj is the dollar value of world trade with country/region j, and Tww is the dollar value of world trade. An index of more than one indicates that trade flow between countries/regions is larger than expected given their importance in world trade.
Trade share is the percentage of trade with a partner to total trade of an economy/region. 'Trade' is the sum of imports and exports.
Trade openness is measured by total trade of an economy expressed as a percentage of nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in dollars. A higher value indicates a more open economy.
Foreign Direct Investment Indicators
Notes: FDI flows in the host economy by geographic origin are sourced from United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) Bilateral FDI Statistics. However, UNCTAD’s Bilateral FDI Statistics is only available up to 2014. FDI inflows data from national sources, ASEANstats Database from Association of Southeast Asian Nations Secretariat, Eurostat Balance of Payments Database were also used. Total FDI inflows data from world for each country are from UNCTAD World Investment Report Statistical Annex. Inward Direct Investment Position (DIP) data are from the International Monetary Fund Direct Investment Positions dataset (formerly Coordinated Direct Investment Survey). Reporter country pertains to the host economy (recipient or destination) of FDI while partner country pertains to the home economy (investor or source) of FDI.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) refers to the category of international investment that reflects the objective of a resident entity in one economy obtaining a lasting interest in an enterprise resident in another economy. A 10 percent ownership of control qualifies as direct investment. Some economies may allow for subjective qualifications, but most foreign direct investment enterprises are branches or subsidiaries that are wholly or majority owned by the nonresident, and borderline cases are likely to be few. Components of direct investment capital transactions are recorded primarily on a directional basis (i.e., resident investment abroad, nonresident investment in the recording economy). Subcomponents of direct investment are equity capital, reinvested earnings, and other capital related to intercompany debt. FDI flows with a negative sign indicate that at least one of the three subcomponents is negative and not offset by positive amounts of the remaining components. These are instances of reverse investment or disinvestment. Inward FDI stock in the reporting economy is the value of capital and reserves (including retained profits) attributable to a parent enterprise resident in a different economy, plus the net indebtedness of affiliates to the parent enterprise. In concept, market price is the basis for the valuation of flows and stocks, but in practice, book value or historical cost is used, reflecting prices at the time when the investment was made. The standard for reporting FDI is the Balance of Payments (BOP) Manual 5th edition and 6th edition starting 2014. Please refer also to the UNCTAD website for FDI definitions, sources, methods, and practices.
-
Inward FDI flows are foreign capital reported as balance-of-payments net inflows. Data is available from 2001 for 47 regional members of ADB except for Nauru.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) share is the percentage of regional FDI inflows to total FDI from the investing region. Data is available from 1995 at the earliest for 26 regional member countries. A higher share indicates a stronger preference for the region and a higher degree of integration.
Inward Direct Investment Position refers to the value of outstanding positions by immediate direct investor, broken down by counterpart economy, and between equity and debt instruments. It is a stock data. Direct investment arises when a unit resident in one economy makes an investment that gives control or a significant degree of influence on the management of an enterprise that is resident in another economy. Data in the DIP are recorded by economy based on the location of the immediate counterpart economy relative to a direct investment position. Please see DIP Guide for more information. Data is available from 2009.