-
- Themes
- Database
- AEIR Data Catalogue
- Free Trade Agreements
- Macroeconomic database:
- Regional Cooperation and Integration database:
- Daily Market Watch
- Resources
- Events
- Economies
- Central Asia
- East Asia
- Oceania
- South Asia
- Southeast Asia
- The Pacific
- COVID-19


Asian Economic Integration Report 2018
This publication is the annual report of the Asian Development Bank (ADB) on Asia’s progress in regional cooperation and integration. It covers ADB’s 48 regional members and analyzes regional and global economic linkages. This year’s special chapter, “Toward Optimal Provision of Regional Public Goods in Asia and the Pacific”, examines how collective action among countries can help find solutions to growing transnational development challenges. It discusses how to best provide regional public goods (RPGs) that transcend the so-called “collective action problem”, which occurs when individual interests are too weak on their own to drive cooperation on common issues. The chapter suggests that multilateral development banks should act as honest broker in enhancing mutual trust and facilitating regional cooperation for RPGs.
The newly-introduced Asia-Pacific Regional Cooperation and Integration Index (ARCII) allows Asian economies to track and monitor the progress of their regional integration efforts across six different socioeconomic dimensions.
Asia remains more financially linked to the rest of the world than to itself.
Amid a slowdown in total inward foreign direct investment to Asia, intraregional investment flows continue to rise.
Firms in Asia are bolstering their status as global investors.
A large part of intraregional FDI is greenfield investment, mainly in manufacturing, while M&As; are more dominant for FDI going outside the region.
Asia’s intraregional trade continued to strengthen, providing a buffer against potential headwinds from global trade and policy uncertainties.
Tourism is growing rapidly in the region, both in terms of the number of tourists and the amount of tourism receipts.
Remittances to Asia declined in 2016, but its impact within the region was varied.
Twenty years after the Asian financial crisis, Asia stands strong—with more flexible exchange rates, higher foreign reserves, healthier financial systems, stronger regulations, deeper capital markets, and better regional financial cooperation mechanisms.
Growing financial interconnectedness can increase vulnerabilities to external shocks, financial contagion, or liquidity risks stemming from cross-border bank lending.
Contents:
Download chapter
Cover and highlights
Download chapterRegional Economic Outlook and Development Challenges
- Economic Outlook and Risks
- Development Challenges: Vulnerabilities to Economic, Environmental, and Social Shocks
- Regional Integration as Development Strategy
Download chapterTrade and the Global Value Chain
- Recent Trends in Asias Trade
- Asias Intraregional Trade
- Progress of Global and Regional Value Chains
- Updates on Regional Trade Policy
- Trade Remedies
Download chapter Download Online AnnexForeign Direct Investment
- Trends and Patterns of Foreign Direct Investment in Asia
- Outward Foreign Direct Investment
Download chapterFinancial Integration
- Asias Cross-Border Financial Assets and Liabilities
- Inward Portfolio Investment
- Outward Portfolio Investment
- Inter- and Intra-Subregional Portfolio Investment
- Bank Holdings
- Analysis Using Price Indicators
- Financial Spillovers
Download chapterMovement of People
- Migration
- Remittances
- International Tourism Receipts and the Movement of Tourists
Download chapterSubregional Initiatives
- Central and West Asia: Central Asia Regional Economic Cooperation Program
- Southeast Asia: Greater Mekong Subregion Program
- East Asia: Support for RCI Initiatives under CAREC and GMS Subregional Programs and Knowledge-Sharing Activities
- South Asia: South Asia Subregional Economic Cooperation
- The Pacific: Building Regional Disaster Resilience through Contingent Financing
- Improving the Provision of Public Goods through Regional Cooperation
Download chapterTheme Chapter: Toward optimal provision of regional public goods in Asia and the Pacific
- Introduction
- Concepts, Typologies, and Issues in Efficient Provision
- Regional Public Goods in Asia
- Measurement Issues and Case Studies on Provision Mechanisms
- Conclusions and Policy Considerations
- Background Papers
Download chapterStatistical Appendix
Infographics:
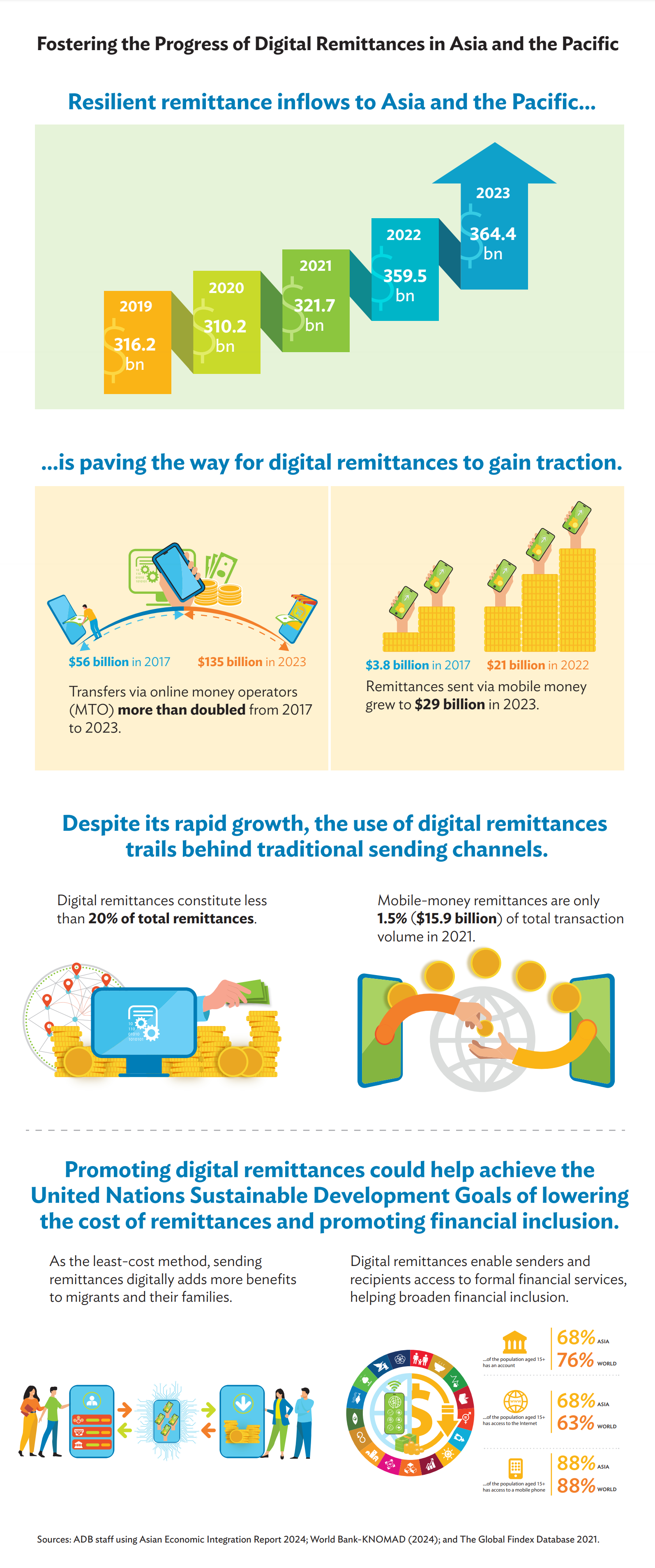
18Dec2024Fostering the Progress of Digital Remittances in Asia and the Pacific
Digitalization contributes to resilient remittance inflows, setting the path to lower remittance costs and greater financial inclusion.
4Jul2023US Dollar Remains Dominant Currency
Trade and financial transactions continue being performed largely in US dollars. Over three-fourths of trade are in US dollars, while roughly 50% of financial transactions are in US dollars.
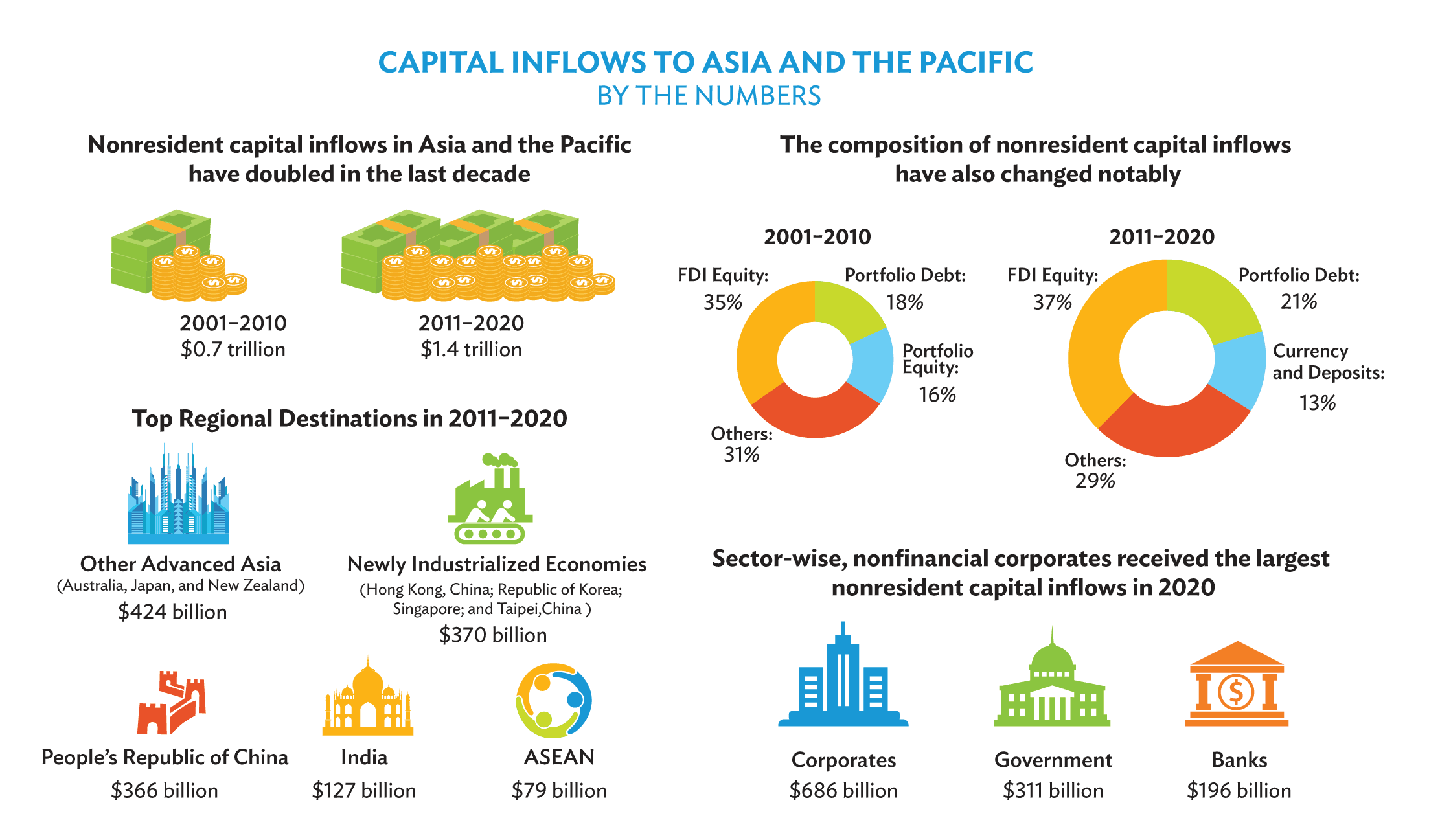
4Aug2022Evolving Patterns of Capital Flows in Asia and the Pacific
Nonresident capital inflows in Asia and the Pacific have doubled in the last decade, with notable changes in the composition and patterns of capital flows.
14Jul2022Global Semiconductor Chip Shortages
Producing semiconductors are highly specialized and geographically concentrated, rendering the sector vulnerable to supply chain disruptions. To ensure supply, an enabling environment research and development (R&D), investments, and skills development are key areas of government intervention.
20May2022The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership
RCEP is the most ambitious application of a rules-based trading system among economies in Asia and the Pacific.
5Apr2022Resilience of remittances to Asia and the Pacific
Remittance inflows to Asia and the Pacific displayed resilience despite the pandemic, propping up limited fiscal space and providing a lifeline to many affected households in the region. Several factors have contributed to this, as explained in Chapter 5 of the AEIR 2022.
AEIR Archives:
ASIA REGIONAL INTEGRATION CENTER© 2015 Asian Development Bank. All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.About usThe Asia Regional Integration Center (ARIC) is an ongoing technical assistance project of the Economic Research and Development Impact Department (ERDI). Following the 1997/98 Asian financial crisis and the contagion evident around the region, ADB was asked to use its knowledge-based expertise to help monitor the recovery and report objectively on potential vulnerabilities and policy solutions. With the ASEAN+3 process just starting, ADB provided technical assistance beginning in 1999—to create the Asia Recovery Information Center, the precursor to ARIC.Contact usPlease help us improve the ARIC website by sending us your comments. These may be on content, (e.g., articles posted on or for which links are provided in the ARIC website), website structure (e.g., do you find ARIC's sections useful?), ease of navigation, or even page design and layout.
Send all your comments to: aric_info[at]adb.orgQuick links
Other ADB sites:
ADB Regional Cooperation and Integration | Asian Bonds Online | Asian Development Bank Institute | RTA Exchange